The Acclima DataSnap is a simple-to-use data recorder. It provides the ability to read and log data from a variety of SDI-12 sensors using a USB port and the Acclima SnapView software. Each DataSnap supports up to 10 SDI-12 sensors.
The DataSnap handles all timing requirements of the SDI-12 communications protocol, making it possible to take SDI-12 sensor readings using a simple terminal program such as HyperTerminal or PuTTy.
DataSnap Hardware Features:
SnapView Software Features:
What is in the box?
The Acclima DataSnap will support all SDI-12 soil water content sensors (probes or meters) that are compatible with version 1.0 through 1.4 of the SDI-12 Protocol Specification when the optional 12VDC Power adapter is attached. The DataSnap is limited to 700mA. Some sensors with higher power requirements may require an external power connection.
NOTE: The DataSnap will not function properly when it is only connected to a USB power source and is reading the older Acclima TDR-315, TDR-315L, or TDR-310S soil moisture sensors. It must also be connected to either the external battery pack or the wall wart (AC to DC adapter) when connected to any TDR-315, TDR-315L, or TDR-310S soil moisture meters due to higher voltage requirements.
The Acclima SnapView software supports all SDI-12 sensor types.
NOTE: Be sure to install the SnapView™ software before connecting the DataSnap to your PC’s USB port!
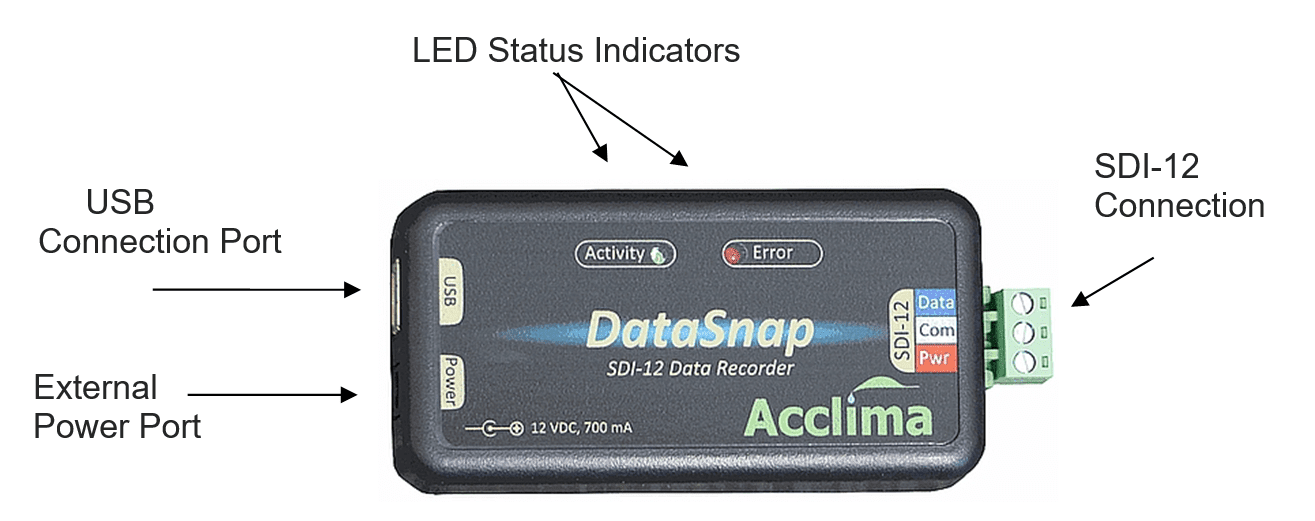
Figure 1
The DataSnap has the following connections:
USB
After software installation, use the included USB cable to connect to a PC.
SDI-12
The terminal block can be unplugged from the DataSnap while wiring sensors together. Multiple sensors can be wired in parallel to the same SDI-12 port.
External Power Port
This connection is provided should the sensor network require higher voltage or current than can be provided by the USB connection. This also allows for autonomous data logging independent of a PC.
The status indicators will light up to indicate activity or status of the DataSnap:
Activity (Green)
OFF = The DataSnap is sleeping or unpowered.
ON = The DataSnap is ready for use and USB connection is established.
Blinking = Data is moving in or out of the USB or SDI-12 Port.
Error (Red)
OFF = No errors
ON = Short circuit or high current on SDI-12 PWR. Voltage will drop until repaired.
Single Blink = SDI-12 communications failure.
The SnapView software must be installed prior to connecting the Data Snap to the computer. The Data Snap requires a Windows™ driver to be installed before use. The driver is installed during the installation of the SnapView software.
Once the software is installed, connect the Data Snap to the computer via a USB cable. Windows™ will automatically detect the new Data Snap hardware and will attempt to find the appropriate driver. This driver installation process will only occur once per Data Snap. Each new Data Snap will follow the same process.
IMPORTANT NOTE: Be sure to install the SnapView™ software before connecting the DataSnap to your PC’s USB port!
The SnapView software can be downloaded from the Solar DataSnap product page.
Click ‘Install Software’ on the window that appears. The Acclima SnapView software and all required hardware drivers will install. Follow the on-screen directions and accept the default options during the installation.
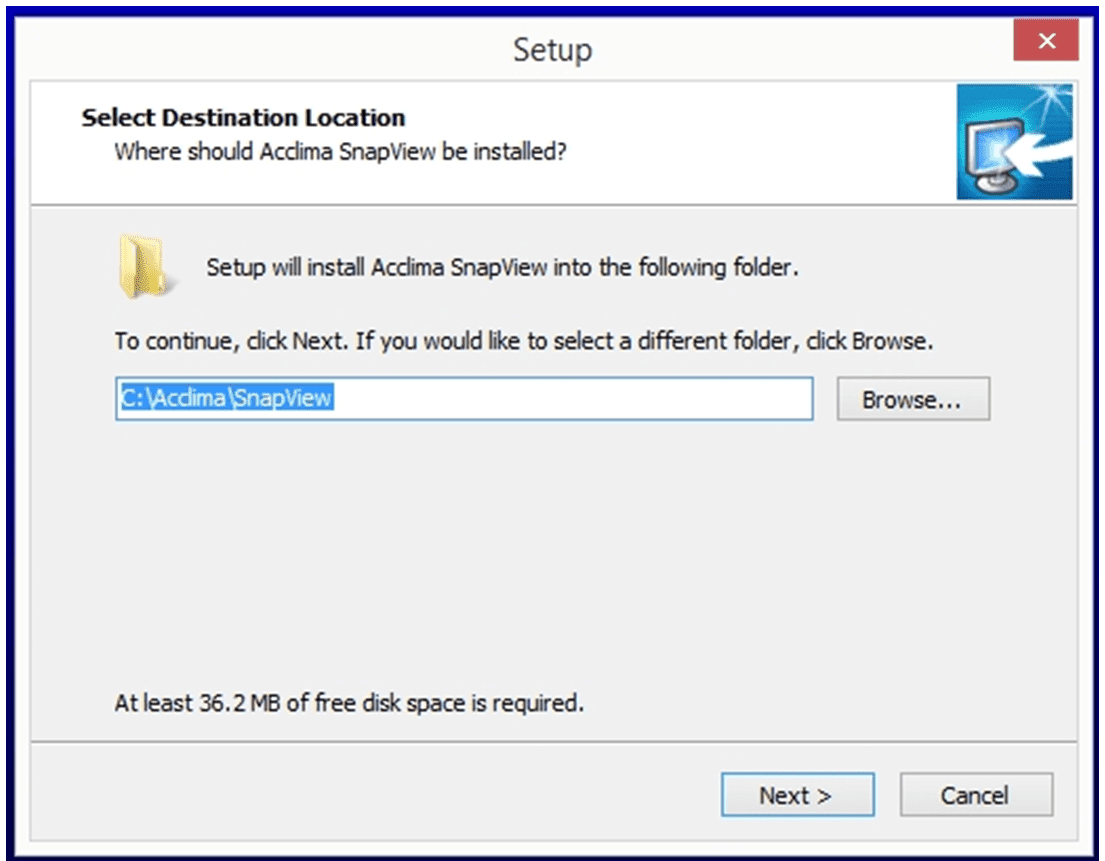
Figure 2
Installing the driver on Windows™
When the Data Snap is first connected to the computer, it will automatically be detected and the installation of the driver will begin.
Windows™ will then search for the driver in its pre-configured driver folders. This will happen because the driver was installed to this location when the SnapView software was installed.
Figure 3
Figure 4
To view more details about the port, open the ‘Device Manger’ in the Control Panel. The Data Snap is visible in the Device Manager under the ‘Ports (COM & LPT)’ heading. The Device Manager only shows ports that are active. When the Data Snap is disconnected from the computer, it will no longer be visible in the Device Manager.
The DataSnap can communicate with and read any type of SDI-12 sensor. It is not limited to Acclima sensors. The DataSnap must be configured to know which sensors to read. This is easily done in the ‘Configuration’ section of the SnapView software. To add sensors, go to the ‘Sensors’ screen and click ‘Add Acclima Sensors’ or the ‘Add a Single Sensor’ at the bottom of the screen.
The SDI-12 protocol does not provide a way to search for multiple connected sensors. Therefore, only one sensor can be connected to the DataSnap when adding a sensor. This is only true for non-Acclima sensors and requires the use of the ‘Add a Single Sensor’ option.
Acclima has engineered a more efficient and intelligent way to configure multiple Acclima sensors simultaneously. This significantly simplifies the configuration process and is done using the ‘Add Acclima Sensors’ option.
The process for adding sensors to a DataSnap is as follows:
To add one or more Acclima sensors to the DataSnap:
Each non-Acclima sensor must be added individually to the DataSnap. To add a non-Acclima sensor to the DataSnap:
Modifying Sensor Settings
Each sensor has its own unique set of reading descriptions which can be modified. This includes a descriptive sensor name and descriptive names for each of the 5 sensor readings. To modify sensor settings, click on the sensor in the ‘Configured Sensors’ list. The details for the selected sensor will display. Make any desired changes and click the ‘Save’ button.
When a sensor is added, its reading descriptions are automatically set based on the defaults for this type of sensor. These default reading descriptions can be modified or removed using the ‘Manage Reading Descriptions’ screen in the Tools menu. If there are no defaults for a particular sensor type, SnapView can automatically create them. This occurs the first time a user enters reading descriptions on the ‘Sensor Details’ window and clicks ‘Save’. For more details, see the ‘Using Acclima SnapView Software’ section later in this document.
Sensor validation is the final step in the configuration process. It provides a simple way to verify that all configured sensors are correctly wired into the DataSnap and match the DataSnap’s configuration.
Connect all configured sensors to the DataSnap and click the ‘Validate’ button. The DataSnap will attempt to find and validate each of its configured sensors. Sensors that are found and match the DataSnap configuration are annotated with a green check mark. Sensors that are not found or do not match the configuration show a red X and an error description.
Sensors should be located in the region of interest where soil moisture measurements are desired. Acclima sensors measure the average volumetric water content over the length of the sensor rods. Sensors can be buried in any orientation and will produce average readings as follows:
When selecting a site for sensor placement, consider the following environmental factors:
The Acclima Soil Moisture sensors report soil moisture as a percentage of the total volume measured. This means that the measured volume of soil should be free of foreign objects or variations that may alter the measurement made by the sensor. Consider the following conditions:

Figure 5
SDI-12 sensors communicate and draw power from the same wires. They share the connection to the DataSnap with all other sensors connected to the same DataSnap. This type of a connection is sometimes called ‘parallel’ or ‘bussed’. Sensors can be spliced or connected together at a single common point or as taps into a longer run of wire. Upon wiring completion:
Consider the following points when wiring sensors:
Figures 6 & 7 – Basic wiring diagram
When connecting many sensors to one DataSnap, a wire splice may be necessary. This can be done by connecting all the red sensor wires to a separate, single wire and then connecting the single new wire to the terminal block in the appropriate position. Follow the same procedure to connect the white and blue wires. When the block is connected to the DataSnap, the location of the colored wires must match the colors on the DataSnap. As an alternative Acclima offers the SDI-12 Port Expander accessory (sold separately from the DataSnap).

Figure 6 – Terminal Block Plug-in
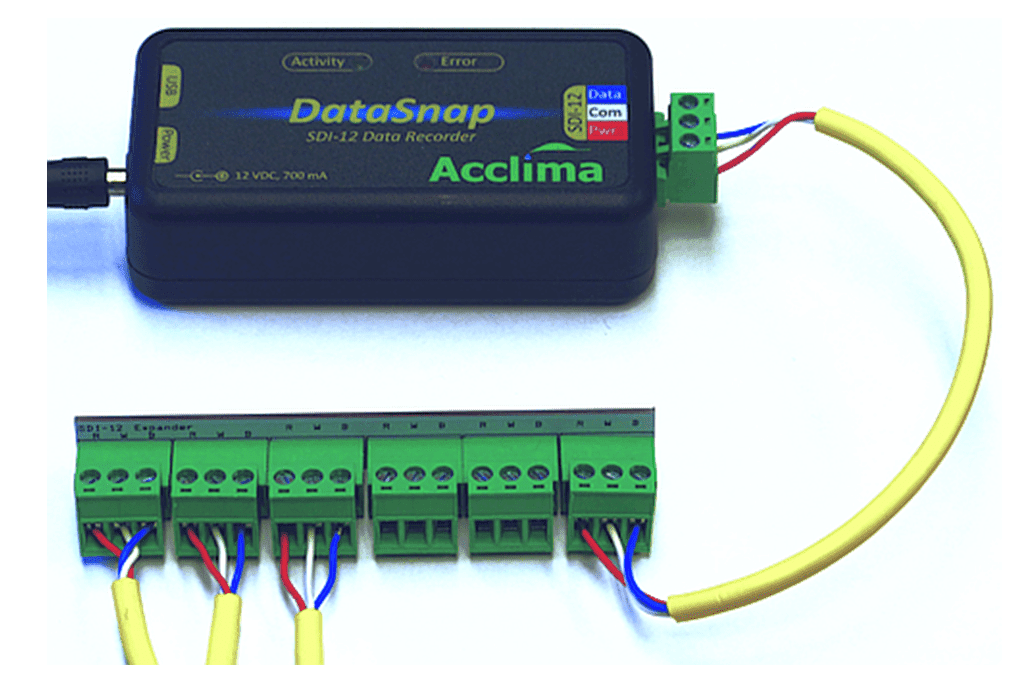
Figure 7 – SDI-12 Port Expander Accessory
Figure 8 – Photograph courtesy of Polycase, Inc.

A DataSnap must be configured prior to its first use. The SnapView software guides you through the configuration process in a few simple steps. To access the Configuration screen, click on the ‘Config’ button at the top of the screen. This will display the Configuration wizard.
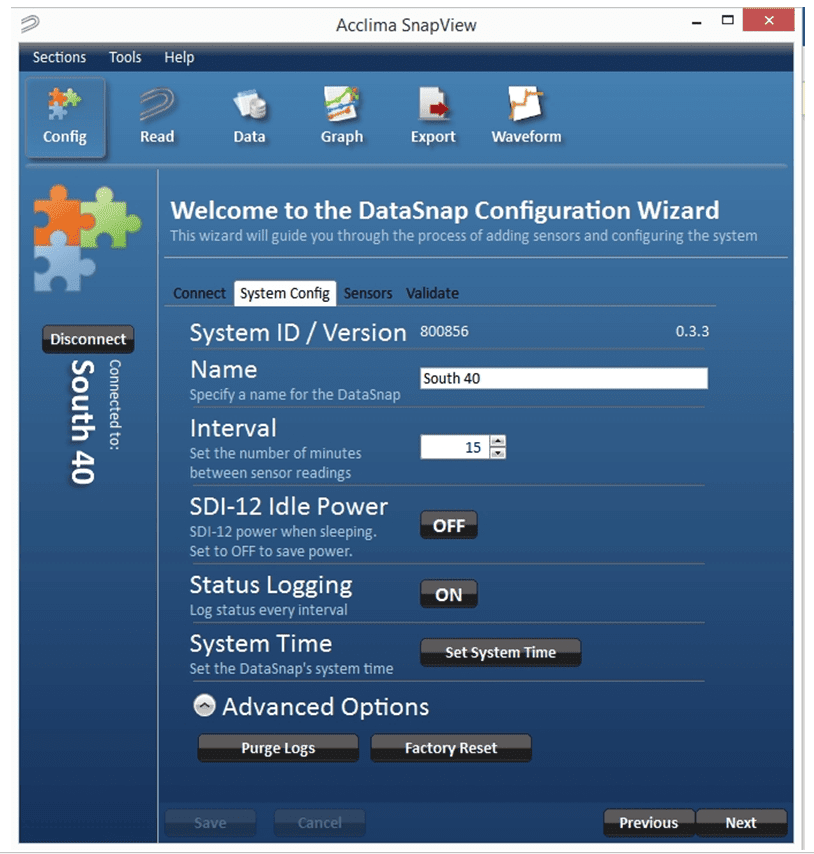
Figure 9 – Configuration
For a DataSnap to automatically take sensor readings or allow a user to read sensors manually, it must be configured. The most important step is to tell the DataSnap what sensors to read. This requires that the sensors be connected to the DataSnap during the configuration process. It is also important to provide a name for the DataSnap and to define how frequently it will take automatic readings. DataSnap configuration settings are stored on the DataSnap and are retained even when power is removed. The configuration wizard is divided into four steps:
The initial configuration screen shows all DataSnaps that are currently connected to the computer. See Figure 12 . To begin configuring a DataSnap, click the ‘Connect’ button next to the desired DataSnap. The name of the connected DataSnap will appear on left side of the screen and the ‘Next’ button is enabled. Use the ‘Next’ and ‘Previous’ buttons to move through the configuration steps. All configuration operations will be performed on the connected DataSnap.
Click the ‘Refresh List” button to scan the computer for DataSnaps and update the connection list.
The system configuration screen allows modification of several DataSnap settings and operations. They are:
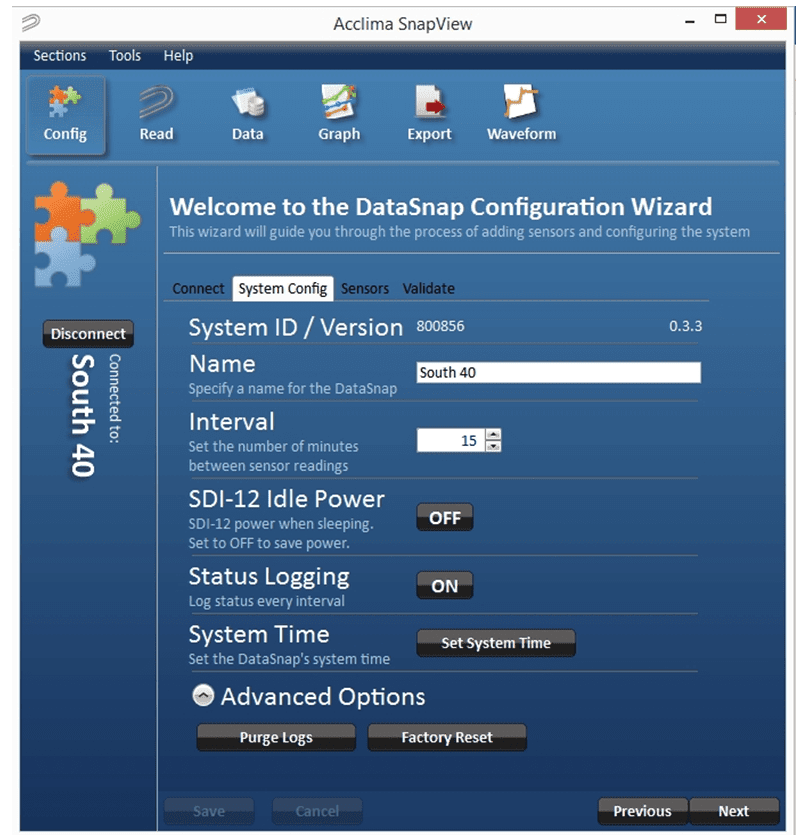
Figure 10 - System Configuration
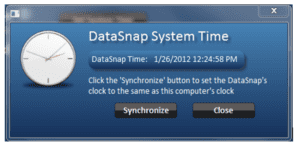
Figure 11 - System Time
The DataSnap can communicate with and read any type of SDI-12 sensor. It is not limited to Acclima sensors. The DataSnap must be configured to know which sensors to read. This is done by adding sensors in the ‘Sensors’ screen. The current list of configured sensors is displayed on the left of the screen. To add more sensors, click the ‘Add Acclima Sensors’ or the ‘Add a Single Sensor’ at the bottom of the screen.
The SDI-12 protocol does not provide a way to search for multiple connected sensors. Therefore, only one sensor can be connected to the DataSnap when adding a sensor. This is only true for non-Acclima sensors and requires the use of the ‘Add a Single Sensor’ option.
Acclima has engineered a more efficient and intelligent way to configure multiple Acclima sensors simultaneously. This significantly simplifies the configuration process and is done using the ‘Add Acclima Sensors’ option.
To add one or more Acclima sensors to the DataSnap:
To add a single, non-Acclima sensor to the DataSnap:
Each sensor has its own unique set of reading descriptions which can be modified. This includes a descriptive sensor name and descriptive names for each of the five readings. To modify sensor settings, click on the sensor in the ‘Configured Sensors’ list. Details for the selected sensor will be displayed. Make any desired changes and click the ‘Save’ button.
When a sensor is added, its reading descriptions are automatically set based on the defaults for this type of sensor. These default reading descriptions can be modified or removed using the ‘Manage Reading Descriptions’ screen in the Tools menu. If there are no defaults for a particular sensor type, SnapView can automatically create them. This occurs the first time a user enters reading descriptions on the ‘Sensor Details’ window and clicks ‘Save’.
There may be times when it is necessary to remove a configured sensor since it is no longer needed or to make room for a new sensor. This is easily done by clicking the ‘Remove Sensor from DataSnap’ button at the top of the ‘Sensor Details’ window. This does not remove any data from the PC, it only removes it from the configuration on the DataSnap.
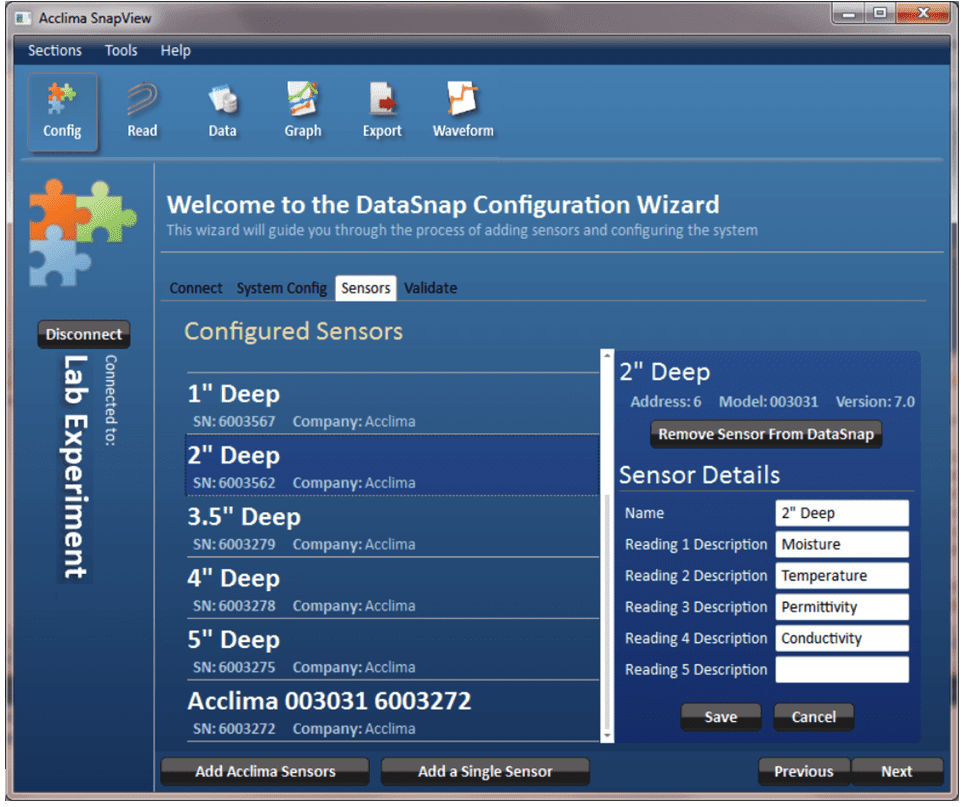
Figure 12 - Adding Sensors
Sensor validation is the final step in the configuration process. It provides a simple way to verify that all configured sensors are correctly wired into the DataSnap and match the DataSnap’s configuration.
Connect all sensors to the DataSnap and click the ‘Validate’ button. The DataSnap will attempt to find and validate each of it configured sensors. Sensors that are found and match the DataSnap configuration are annotated with a green check mark. Sensors that are not found or do not match the configuration show a red X and an error description. See Figure 13 .
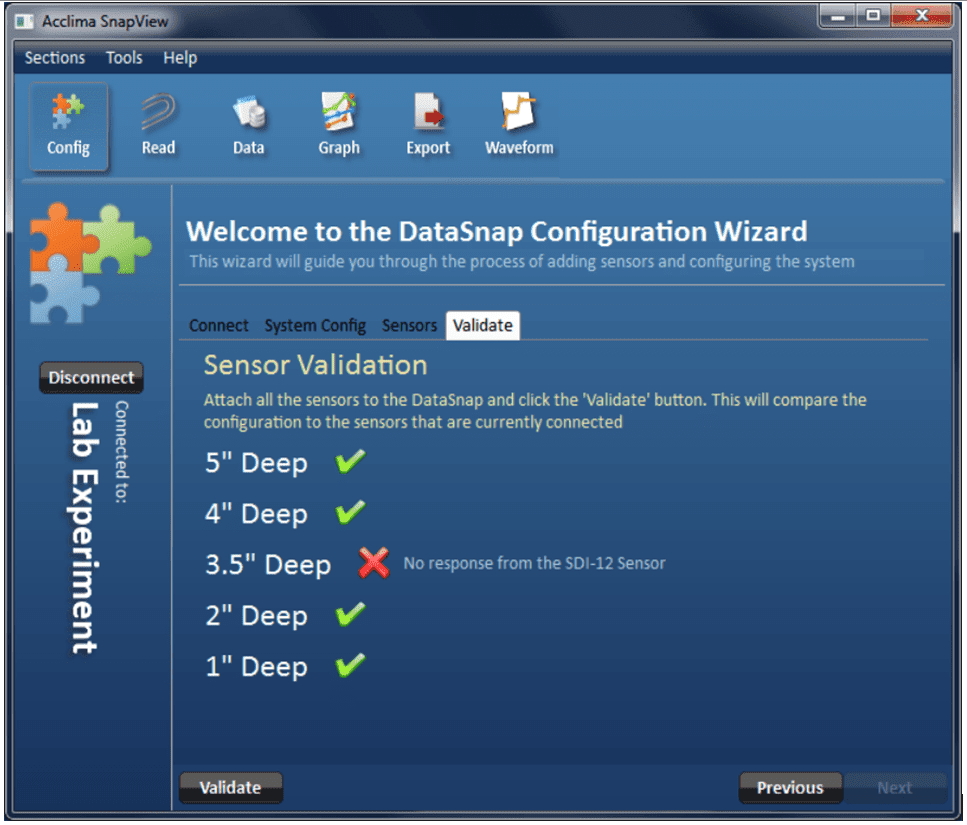
Figure 13 - Sensor Validation
Figure 14 - Synchronization

Each DataSnap can accommodate up to 10 sensors. The connected sensors can be manually read at any time. Prior to reading any sensor, the sensor must be connected to and configured on the DataSnap. This is a one-time process and is covered in detail in the ‘Configuration’ section. Manual readings do not occur automatically and are not saved for historical analysis.
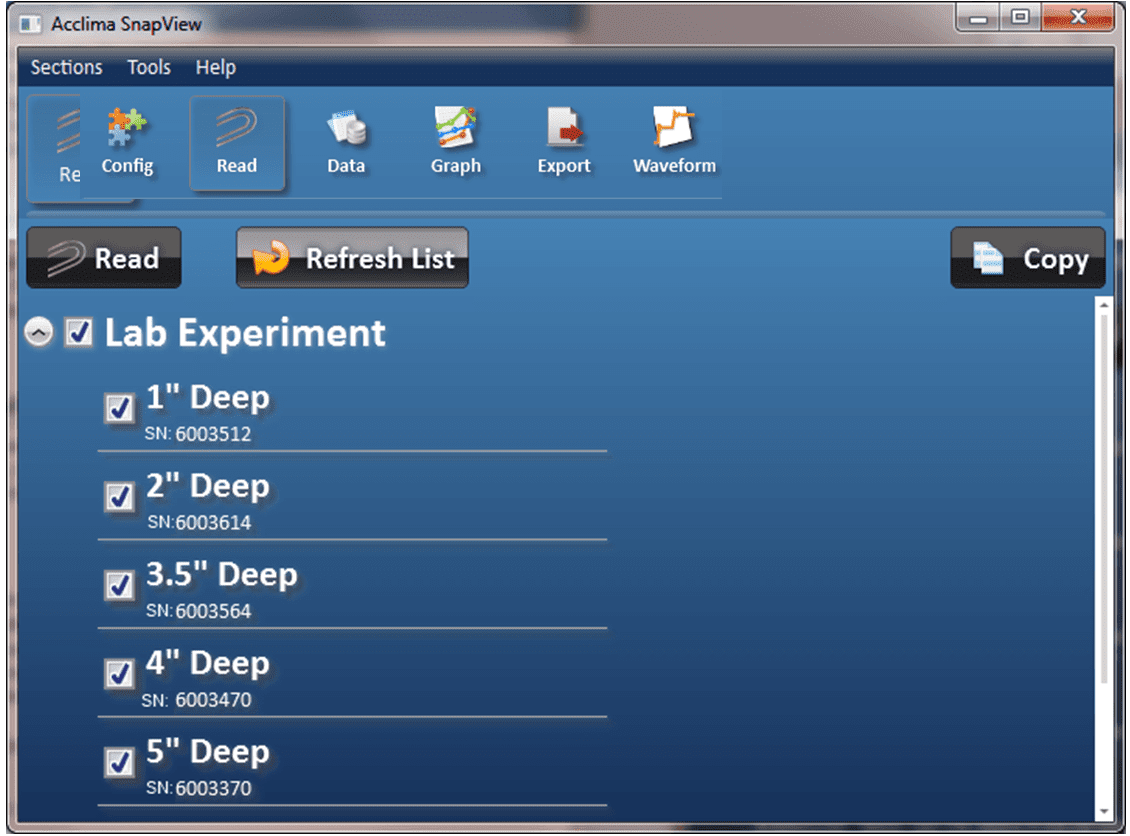
Figure 15 - Initial Read Sensor Screen
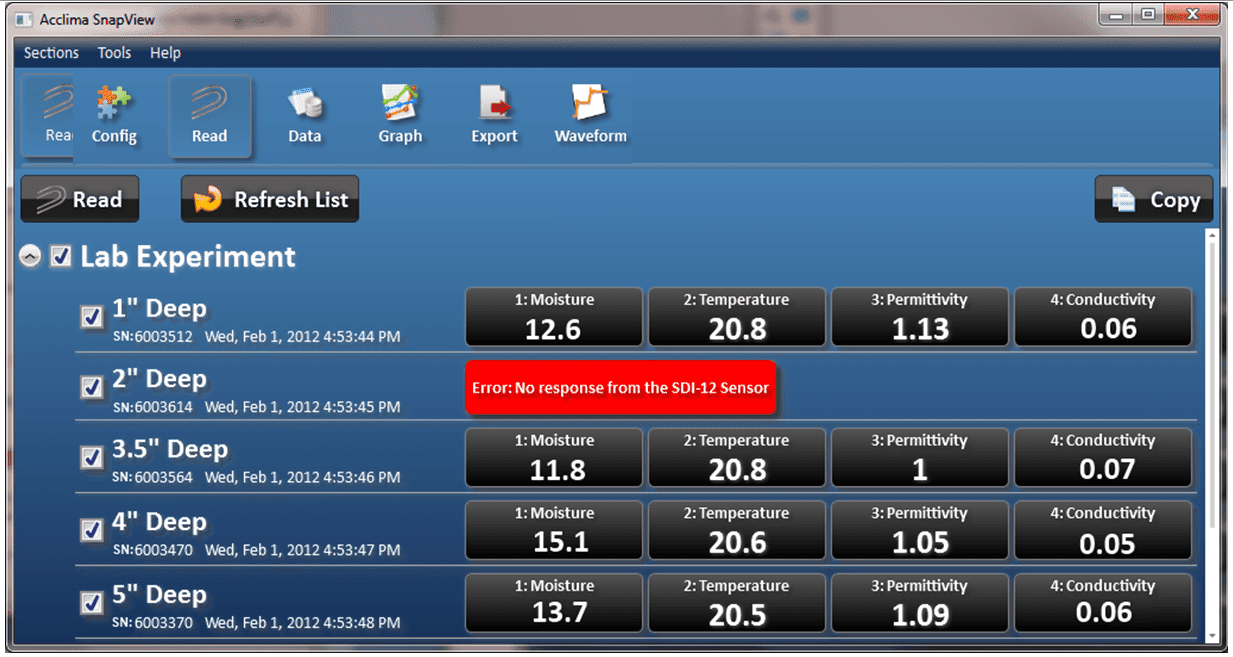
Figure 16 – Read Sensors

Sensor readings for all sensors can be viewed visually through the ‘Graph’ screen. To see the ‘Graph’ screen, click on the ‘Graph’ button at the top of the screen. The graph view allows access to the historical data of each DataSnap that has ever been connected to this PC. It does not require a DataSnap to be connected.
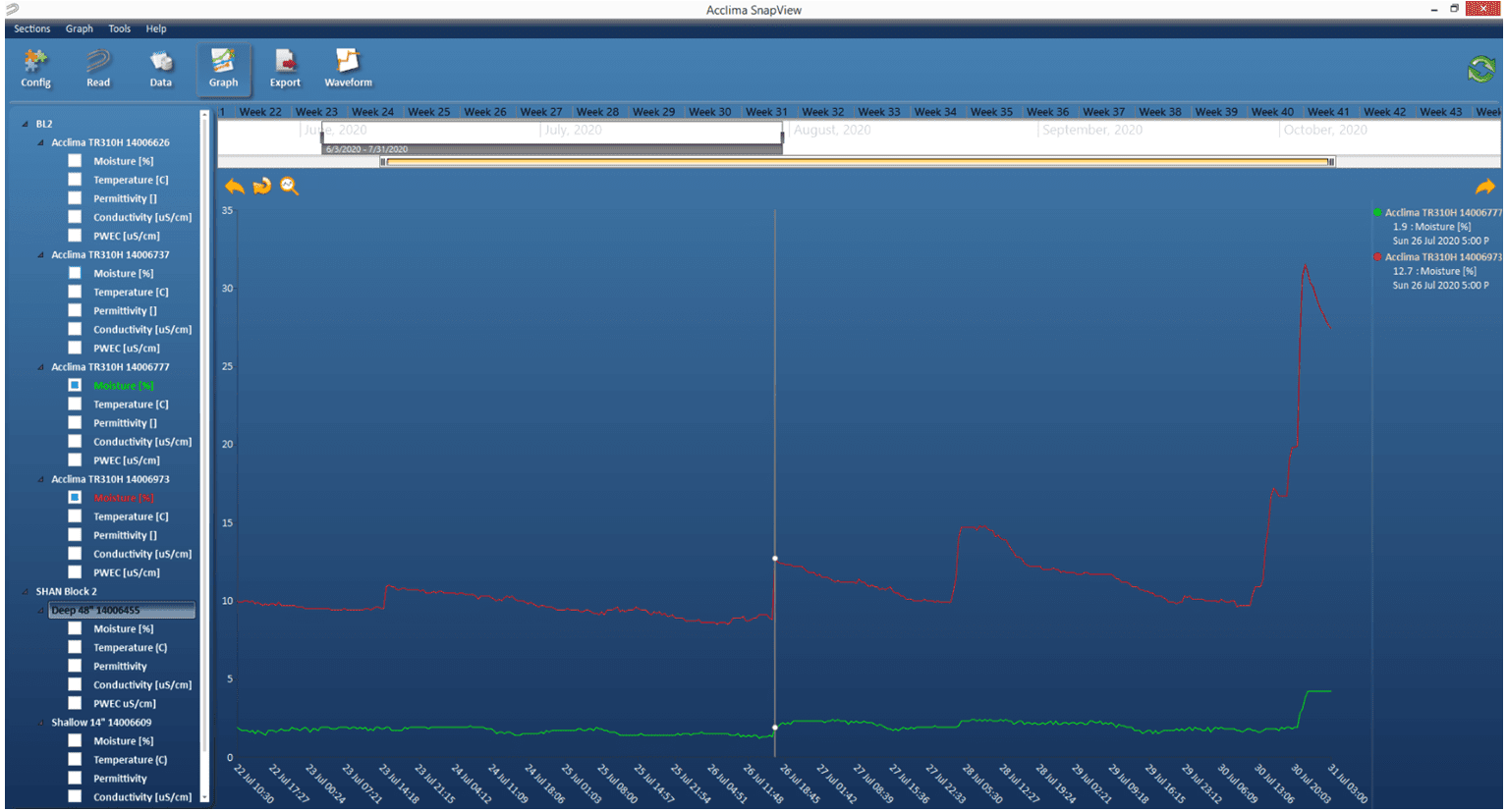
Figure 17 – Data in Graph View
The Graph view has three main sections.
Click the ‘Graph’ button at the top of the screen.
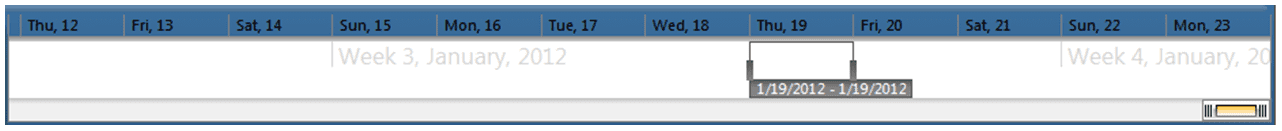
Figure 18 – Date/Time Selection

Figure 19 – Time Bar Selection Window
The date range can be adjusted by dragging the gray rectangles on the right and left boundaries of the range selection window. Dragging the left most range indicator to the left will change the displayed start date in the main graph to an earlier date. Dragging it to the right will change the displayed start date in the main graph to a later date. The right most range indicator behaves similarly and effects the end date on the main graph. The selected date range is displayed immediately below the range selection window.
To maintain the same number of days in the date range but to see a different range, simply click anywhere in the selection window and drag it to the right or left.
To select a single day, click on the date in the blue region at the top of the time bar. As an example, Figure 19 shows that January 19, 2012 has been selected. To select multiple full days, left click on a date and while holding down the left mouse button, drag to another date and release the button. The selection range will be highlighted in yellow as the mouse is dragged. The selection window will now change to the range that was selected. As an example, Figure 20 shows how the time bar would look while clicking ‘Wed, 18’ and dragging to ‘Fri, 20’. Once the mouse is released, the range selection window will move and the main graph will display data for the three selected days.
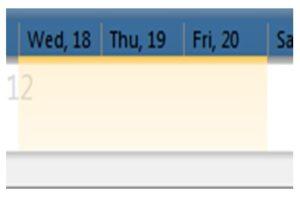
Figure 20 - Selecting Multiple Days in the Time Bar
Figure 21 - Time Bar Scrollbar Showing Months
Figure 22 - Time Bar Scrollbar Showing Days

Sensor readings can be viewed in a spreadsheet format in the ‘Data’ screen. Click on the ‘Data’ button to access the ‘Data’ screen. The data view allows access to the historical data of each DataSnap that has ever been connected to this PC. It does not require a DataSnap to be connected.
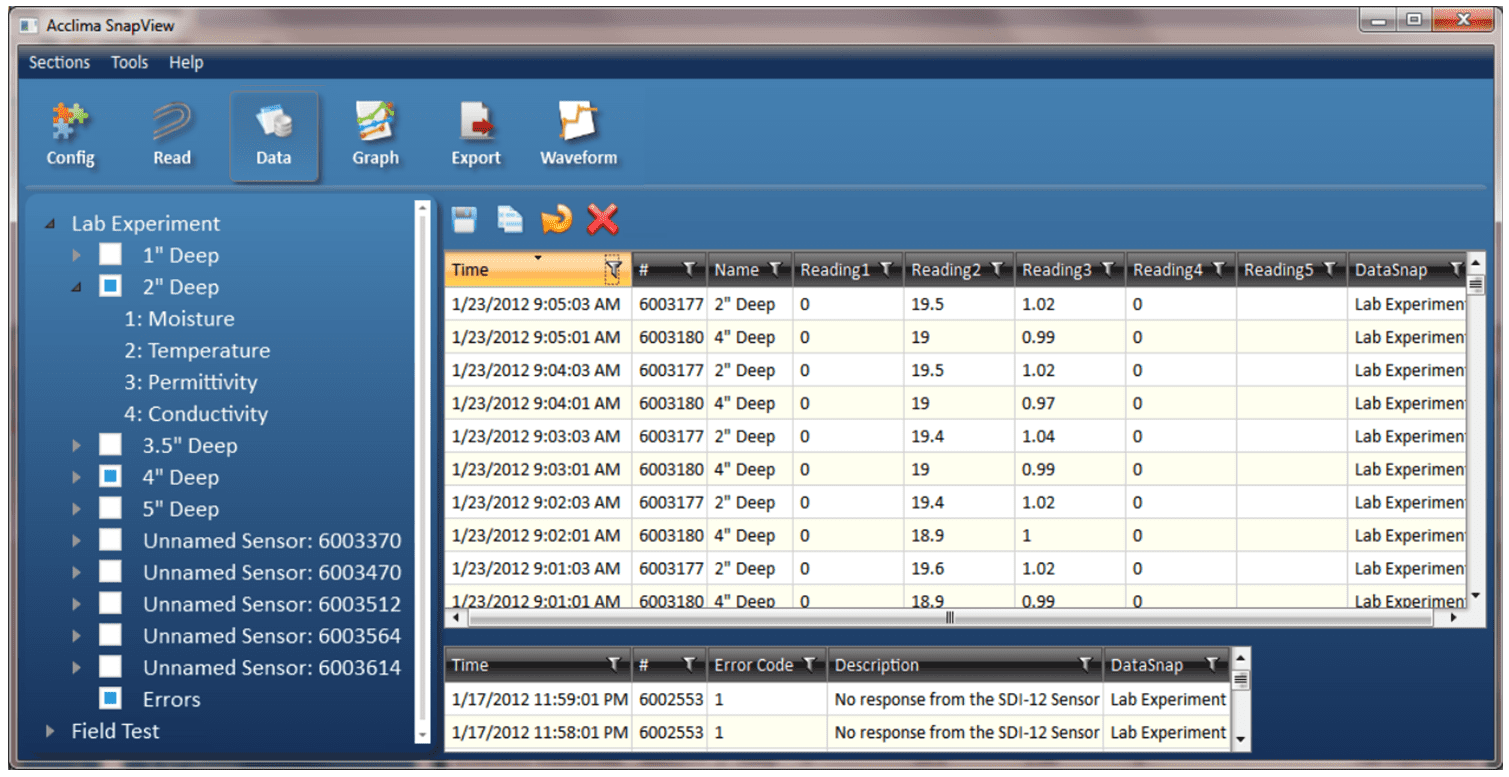
Figure 23 – Data in Grid View
There are several different operations that can be performed within the data screen. These are accessed via the options bar. They include:
To sort data in each column, click anywhere on the black column header. The data will now be sorted by that column heading. Clicking the header again will sort the column in the reverse order.
A filter may be applied to limit the amount of data displayed. Each column can be filtered and multiple columns may be filtered at the same time. To specify a filter for a column, click on funnel shaped icon in the header of the column. If the icon is white, no filter has been applied. If the icon is yellow, a filter has been applied.
In Figure 24 , a filter has been applied for the ‘Name’ and ‘Reading 1’ columns but not the ‘Reading 2’ column.

Figure 24 – Grid Filter Indicator
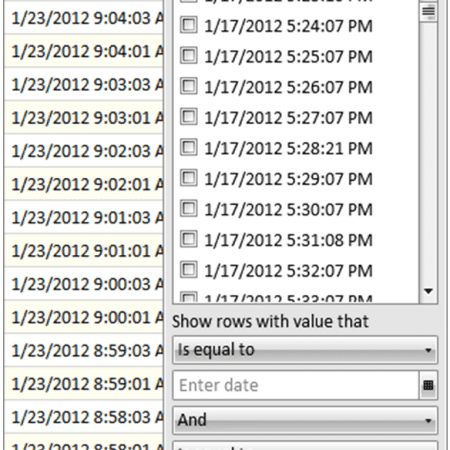
Figure 25 – Filter Window for the Time Column
The filter window displays a list of items that are available for display. Each item can be selected or not selected as desired. If an item is selected, it will be displayed in the grid. If it is not selected, it will be hidden in the grid. To select all items, click the ‘Select All’ option near the top of the filter window. Clicking the ‘Select All’ option a second time will deselect all items.
The list of items is dependent on the data in the column. Other custom filter criteria can be specified for complex scenarios. These are defined in the lower half of the filter window. These options allow range-based filtering. For instance, a filter could be set that displays all times between January 15, 2012 and January 18, 2012.
To remove the filter, click the ‘Clear Filter’ button.

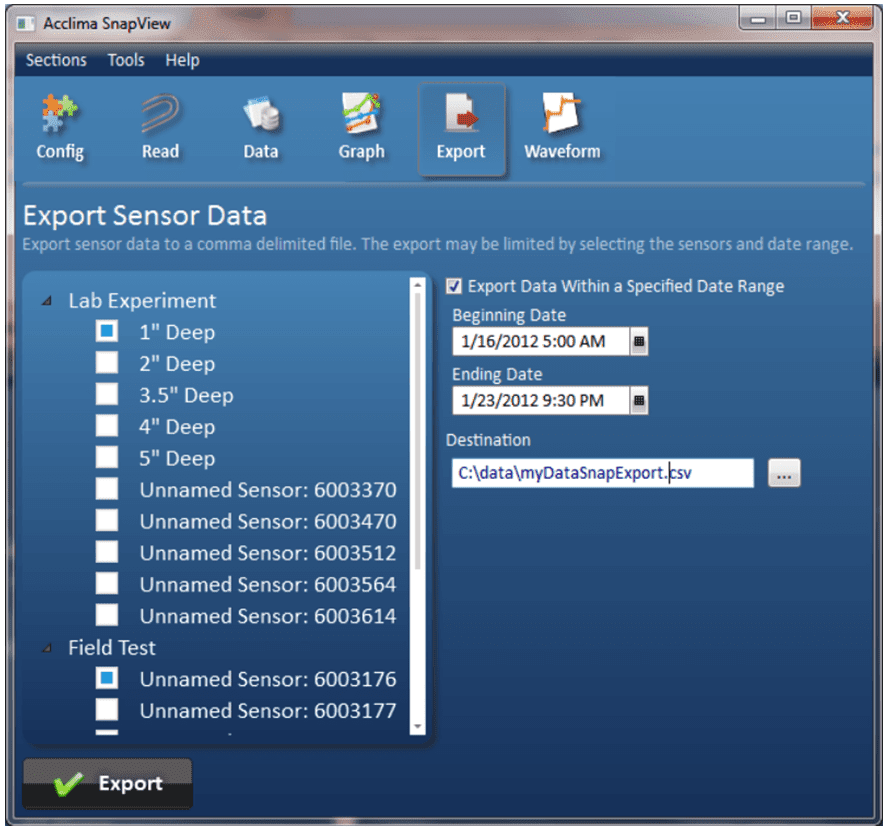
Figure 26 - Data Export
As an example, in Figure 26 , two sensors have been selected. The first selected sensor is named ‘1” Deep’ and is associated with the DataSnap named ‘Lab Experiment’. The second selected sensor is named ‘Unnamed Sensor: 6003176’ and is associated with the DataSnap named ‘Field Test’. Only data between 5am on January 16, 2012 and 9:30pm on January 23, 2012 will be exported. The output file will be named myDataSnapExport.csv and will be saved in the ‘C:\data\’ folder.
The tools menu contains several features. They include:
Acclima TDT and TDR sensors all use time-domain analysis of an electromagnetic wave propagated along the waveguide to derive measurement data. Some scientists or advanced users may wish to do their own analysis of waveform data, and so the Waveforms feature was added to the SnapView software to provide access to sensor waveforms. To access this new feature, the SnapView software and connected logging devices (DataSnap and Solar DataSnap) may need to be upgraded.
To run the Waveform Capture module in the SnapView software you will need to download and run the latest version of SnapView for Windows®. As of this writing, the latest version of SnapView is 1.4.1. The software can be downloaded here.
When the Waveforms view activates, the SnapView software will begin scanning all connected loggers and sensors to find devices that can support Waveform Capture. The software will prompt you to upgrade the logger firmware if Waveform Capture is not supported by the current logger firmware.

Figure 27 – Firmware Upgrade Prompt
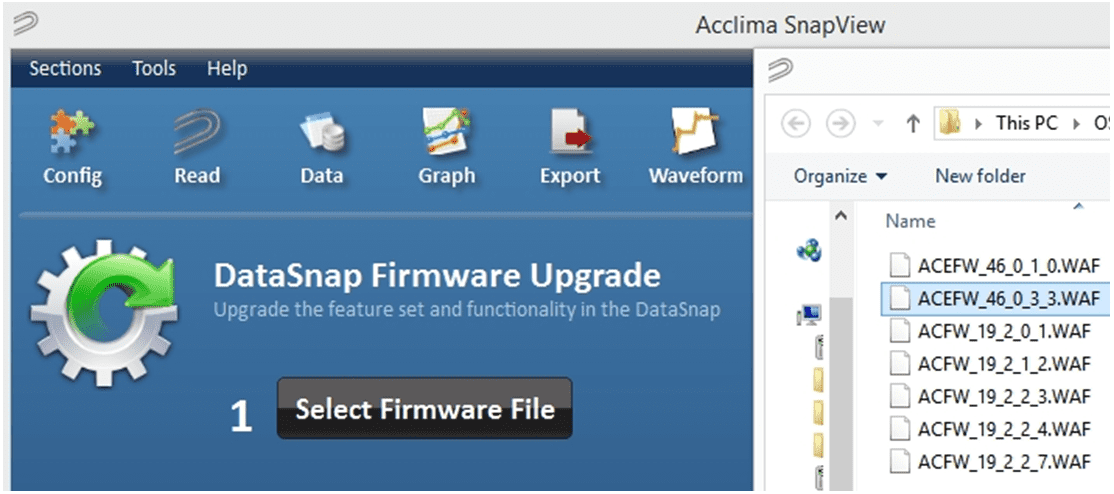
Figure 28 – Select Firmware
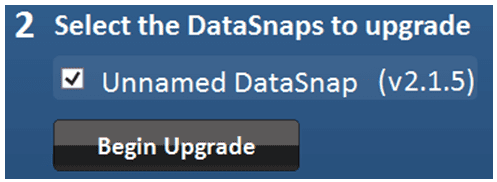
Figure 29 – Select DataSnap and Begin Upgrade
Once you have selected the proper firmware and clicked ‘Open’, left click the ‘ Begin Upgrade ’ button. You will then see a status bar for a few seconds while it progresses to 100%. A message box will then appear indicating that the upgrade was successful.
To open the waveform capture module in SnapView, click the ‘Waveform’ icon.

Figure 30 – Open Waveform Module
 or is immediately shown, you may left click the ‘Stop’ button to stop the list from refreshing further.
or is immediately shown, you may left click the ‘Stop’ button to stop the list from refreshing further.
Figure 31 – Refresh List
With the sensor selected, left click the ‘Get Waveform ’ button to start the waveform graphing. A maximum of 12 waveforms can be displayed at the same time.
Waveform Capture enabled sensors
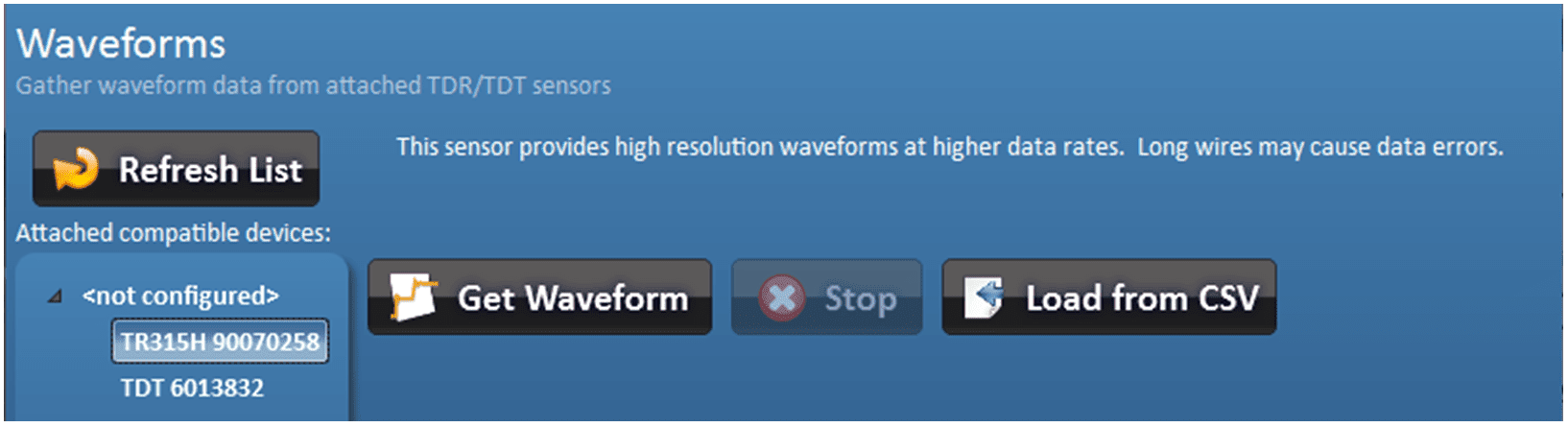
Figure 32 – Get Waveform

If you pull a waveform using an Acclima TDR that has “Waveform Capture ” printed on the label, the entire waveform at full resolution should show up within several seconds of clicking the ‘ Get Waveform’ button.
If you are using an older Acclima soil moisture sensor without the designation of being able to capture a waveform, you can still collect a waveform by selecting that sensor in the list and left clicking ‘ Get Waveform ’ button. The capture will begin, but due to the older design of the sensor it may take approximately 15 minutes to generate the graph. If you find that the capture is taking too long, you can cancel the capture by left clicking the ‘ Stop’ button.
You are also given options to adjust the data that is collected to speed up the collection process.
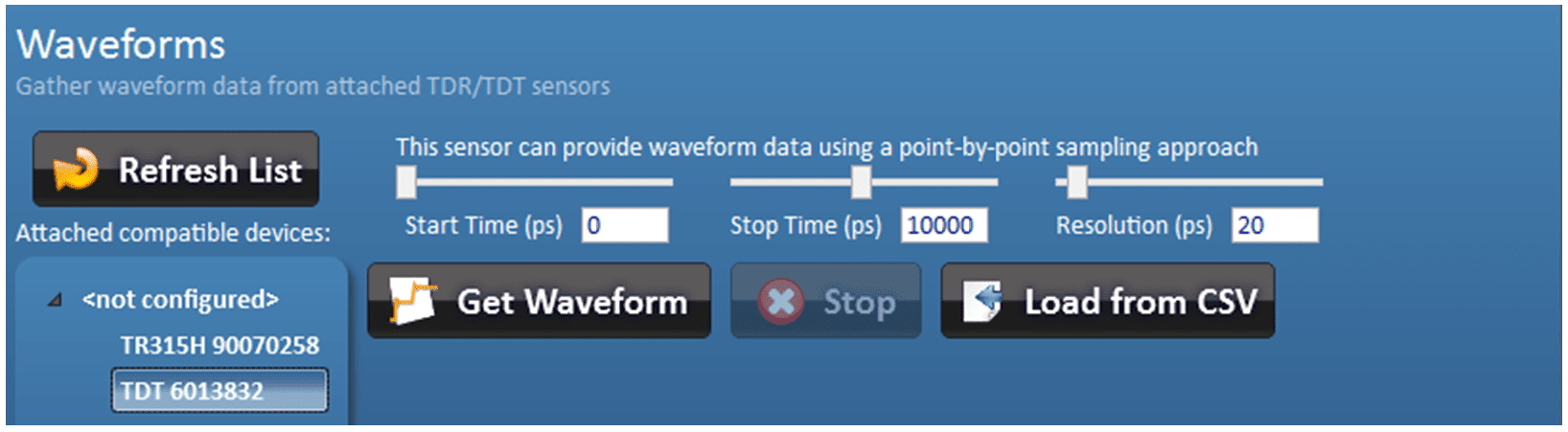
Figure 33 – Getting Waveforms From Older Sensors
The start time, stop time, and resolution of the gathered data (in picoseconds) can be adjusted by moving the sliders or by entering the desired value in the boxes provided. All times are in 5 picosecond steps.
Once the desired parameters have![]() been entered, click the ‘Get Waveform’ button to begin the process.
been entered, click the ‘Get Waveform’ button to begin the process.
A waveform graph will then will begin to be generated similarly to the picture below, (time can vary from a few seconds to 15 minutes depending on whether you are getting a waveform from a sensor labeled with “Waveform Capture” or not):
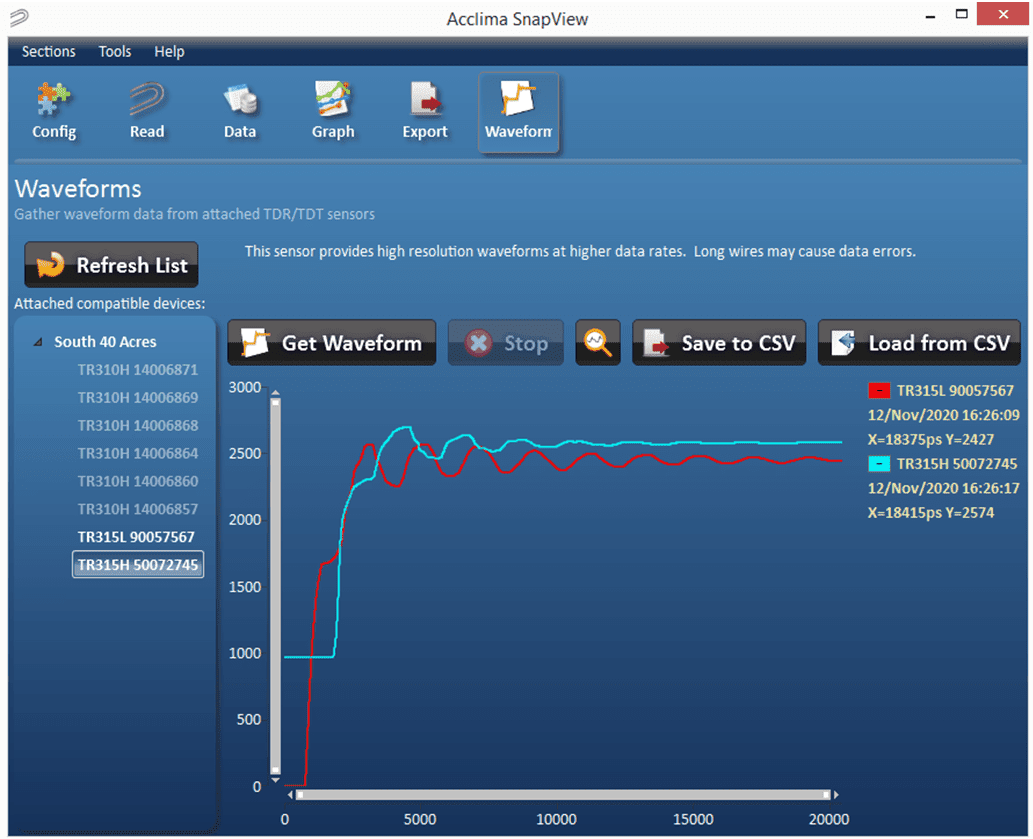
Figure 34 – Waveform Graphs
The waveform line will be color coded to the sensor from which the waveform was taken with the serial number and timestamp legend. Subsequent waveforms taken from different sensors will show up with different color codes and an extended legend.

Figure 35 – Waveform Legend
The minus within the colored (e.g., red) box in the legend can be used to delete the waveform when left-clicked with the mouse.
The user can left click drag a square from upper left to lower right direction over a section of the waveform that needs closer inspection.  A zoomed-in presentation of that waveform section will appear after releasing the left mouse button. To reset the graph to the full view mode just left click the ‘Reset zoom’ (magnifying glass icon).
A zoomed-in presentation of that waveform section will appear after releasing the left mouse button. To reset the graph to the full view mode just left click the ‘Reset zoom’ (magnifying glass icon).
The X, Y axis can be lengthened or shortened with the mouse pointer by hovering the mouse pointer over the end of the X or Y scroll bar until a double ended arrow appears.
⇳ or ⬄
Pressing and holding the left mouse button at that point will grab the end of the scroll bar to allow lengthening and shortening of the scroll bar which zooms in and zooms out. Left clicking the ‘Reset zoom’ (magnifying glass icon) will return the graph to full view.
A waveform or several waveforms can be exported![]() to a CSV file by left clicking the ‘Save to CSV’ file.
to a CSV file by left clicking the ‘Save to CSV’ file.
At this point the save dialog box will appear and you will have the ability to choose the folder in which to save the waveform information. You will also be able to change the name from the default. The default file name is
‘WaveformCollection_YYYYMMDD_HHMMSS.csv’, where YYYY is the year, MM is the month, DD is the day of the month, HH is the hour of the day in 24-hour format, MM is the minute, and SS is seconds – all indicating the date and time that the ‘Save to CSV’ button was pressed.
A waveform graph can be loaded from a CSV file by ![]() left clicking the ‘Load from CSV’ button.
left clicking the ‘Load from CSV’ button.
An open file dialog file will appear allowing you to navigate to the desired CSV file. Once selected, left click ‘Open’. The waveform(s) in the csv file will then be added to the current collection of waveforms already on display, up to a maximum of 12 waveforms. If the csv file contains more than 12 waveforms, manual deletion of row data may be required by the user to display waveforms further down the list.
The load function supports 2 CSV formats:
Length: 4.0” (10.3 cm)
Width: 1.9” (5.0 cm)
Height: 1.2” (2.75 cm)
Operating Temperature: -20 to +60 °C (-4 to +140 °F)
Humidity: 0 to 90% RH, non-condensing
USB Port
Input Voltage: 5VDC, ±0.5V
Input Current: 700mA Max
External Supply Input (optional)
Input Voltage: 6-12VDC, 15V Absolute Max
Input Current: 700mA Max
Connector Type: 2.1mm barrel, center positive
SDI-12 Output
Signal Voltage: Typically 0-5VDC
Power Output Voltage: (Input Voltage) – 0.5V. Voltage may drop when short circuit protection is active
Short Circuit Current: 700mA ±20%
Power Consumption (12V External Power Supply)
35mA: USB Active, No Load/Sensors
8mA: USB Disconnected, Logger Active
1.1mA: USB Disconnected, Logger Sleeping, IDLE_POWER=ON (Output Active, No Sensors)
60uA: USB Disconnected, Logger Sleeping, IDLE_POWER=OFF (Output Power Off)
When the DataSnap is properly installed on a computer USB port, it will implement a generic COM port on that computer. This COM port should be visible in Device Manager as ‘Acclima Virtual COM port’. The communications settings for this COM port are unimportant, and can be ignored, since the output of the DataSnap is fixed as the SDI-12 protocol. This means that the DataSnap will operate regardless of the BAUD rate, stop bits, parity, or Flow control settings. Interfacing with the DataSnap requires software that can open and send/receive data over a COM port.
The DataSnap transfers SDI-12 commands from the USB port to the SDI-12 port without modification to the command string. However, any required Break signals, address mark, or other timing specific requirements are handled by the DataSnap. This removes the burden of SDI-12 timing from the computer, and simplifies the programming requirements for computer software, while providing a modern USB interface. Due to this architecture, all SDI-12 commands and capabilities are present when using the DataSnap, provided that the software using it is not limited. The SnapView software provided with the DataSnap can communicate with all types of SDI-12 sensors and is not limited to Acclima sensors.
Contact [email protected] with questions.
Acclima, Inc.
1763 West Marcon Lane, Ste. 175
Meridian, ID 83642 USA
www.acclima-me.com



Copyright Acclima ©, Inc. All rights reserved.